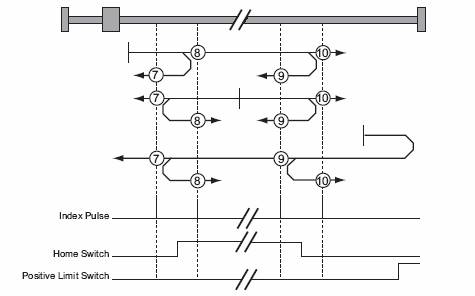
These methods use a home switch, which is active over only a portion of the range of travel. In effect, the switch has a ‘momentary’ action as the axis sweeps past the switch.
In methods 7 to 10, the initial direction of movement is to the right, and in methods 11 to 14, the initial direction of movement is to the left except if the home switch is active at the start of the motion. In this case the initial direction of motion is dependent on the edge being sought. The home position is at the index pulse on either side of the rising or falling edges of the home switch, as shown in the following two diagrams. If the initial direction of movement leads away from the home switch, the drive must reverse on encountering the relevant limit switch.
In all of these methods, encountered a hardware stop limit is treated in the same fashion as the corresponding limit switch becoming active. That is, hardware limit stops can be used in place of the limit switches if desired. Limit switches can be detected more reliably than hard stops, but these switches do add cost to the system.

Figure 7: Homing Off the Home Switch and Index Pulses – Positive Initial Move
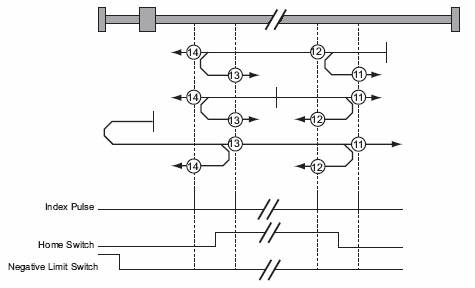
Figure 8: Homing Off the Home Switch and Index Pulse – Negative Initial Move